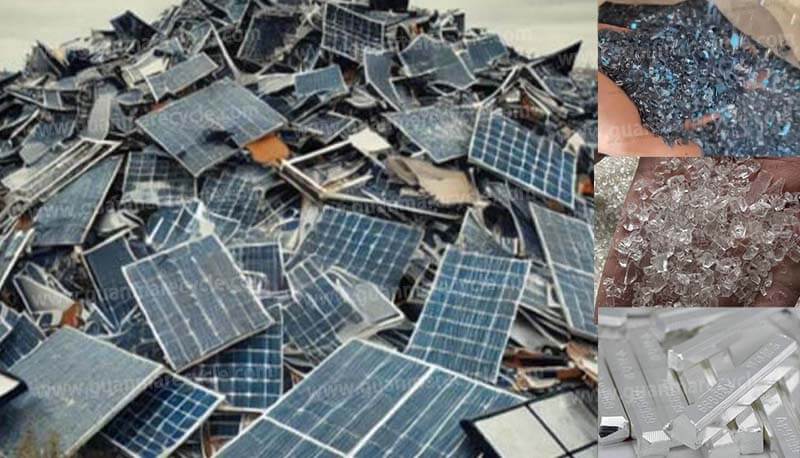
Why India is the Ideal Destination to Set Up a Li-ion Recycling Plant
The global shift toward renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked an urgent need for sustainable solutions to manage lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery waste. As India accelerates its transition to clean energy, setting up a li-ion recycling plant in the country presents a strategic opportunity for businesses to address environmental challenges while tapping into a rapidly growing market.
1. Rising Demand for Li-ion Recycling in India
India’s EV market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 36% by 2030, driven by government initiatives like the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme. With this surge comes an inevitable wave of spent Li-ion batteries—estimated to reach 500,000 tons annually by 2030. However, less than 5% of these batteries are currently recycled, creating a critical gap in waste management infrastructure.
A Li-ion Recycling Plant in India can bridge this gap by recovering valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for producing new batteries.

2. Government Incentives and Policy Support
India’s government actively encourages sustainable industries through policies and subsidies:
Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme: Offers financial
incentives for advanced chemistry cell (ACC) battery manufacturing, including recycling.
E-Waste Management Rules 2022: Mandates battery producers to ensure safe recycling, creating a steady demand for certified recyclers.
3. Cost-Effective Labor and Infrastructure
India’s competitive operational costs make it a cost-efficient hub for recycling operations:
Skilled Workforce: A large pool of engineers and technicians trained in mechanical processes.
Affordable Land: Industrial zones in states like Gujarat, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu offer subsidized land for green projects.
Strategic Logistics: Proximity to ports simplifies the export of recycled materials to global markets.
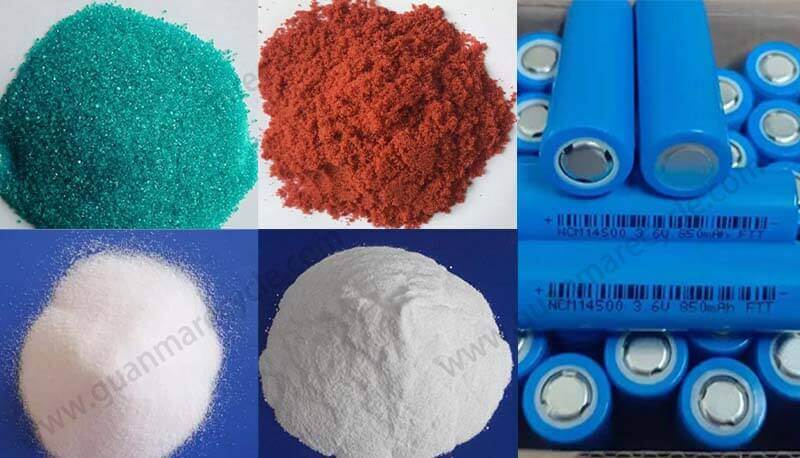

4. Environmental Impact and ESG Compliance
Establishing a Li-ion Recycling Plant in India supports global Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals:
Reducing Pollution: Proper recycling prevents toxic battery components from contaminating soil and water.
Carbon Footprint Reduction: Reusing metals cuts greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to mining raw materials.
5. Steps to Establish a Li-ion Recycling Plant in India
a) Market Research
Identify high-demand regions (e.g., EV manufacturing hubs in Maharashtra, Telangana) and analyze competitors.
b) Technology Selection
Invest in advanced hydrometallurgical or pyrometallurgical processes for higher metal recovery rates (up to 95%).
c) Partnerships
Collaborate with EV manufacturers, battery producers, and e-waste aggregators for a steady supply of spent batteries.
d) Funding
Leverage government grants, international green funds, or joint ventures with local players.
Seize India’s Li-ion Recycling Opportunity
India’s booming EV sector, supportive policies, and cost advantages make it a prime destination for establishing a Li-ion Recycling Plant.