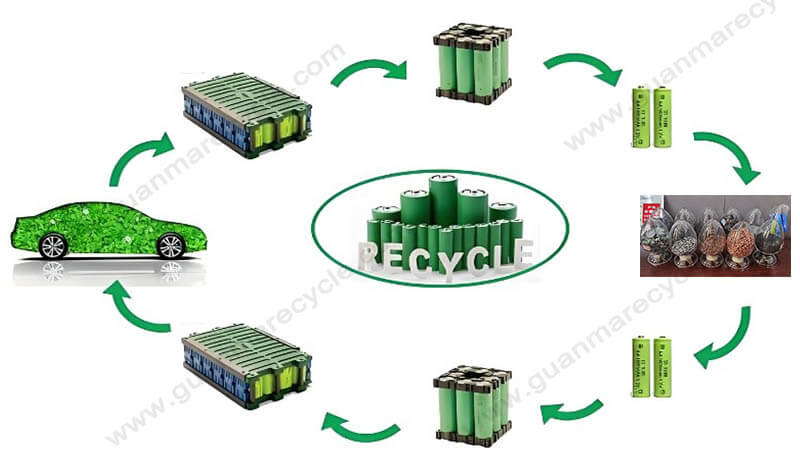
Lithium Ion Battery Recycling Process Introduction:
As the world increasingly embraces renewable energy sources, lithium ion battery recycling has become a vital practice. With millions of batteries powering electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops, and other devices, effective recycling processes are crucial for minimizing environmental impact and recovering valuable materials.
Collection and Pre-Sorting
Gathering Spent Batteries: The first step in lithium ion battery recycling is collecting used batteries from various sources. Collection points can be found at retail stores, recycling centers, or through manufacturer take-back programs.
Pre-Sorting: Upon arrival at a recycling facility, batteries undergo pre-sorting based on chemistry, size, and condition. This ensures that only suitable batteries enter the recycling process, enhancing efficiency and safety.
Discharge and Dismantling
Safe Discharge: Before processing, it’s essential to fully discharge the batteries to eliminate any residual charge. This prevents potential hazards during subsequent stages.
Dismantling: Skilled technicians carefully dismantle the batteries to separate components such as the casing, terminals, and connectors. For certain types, automated machinery may assist in this delicate process.
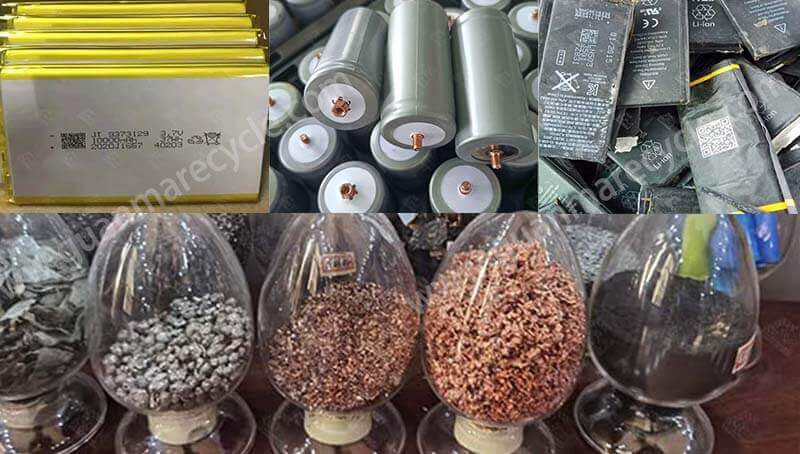

Mechanical Processing
Shredding: In this stage, the batteries are shredded into smaller pieces using specialized equipment. Shredding facilitates the separation of different materials within the battery.
Magnetic Separation: Ferrous metals like steel are separated using magnets, while non-ferrous metals such as aluminum and copper are isolated through other techniques.
Air Classification: Lighter materials, including plastics and separators, are sorted out by air classifiers, leaving behind valuable metal powders.
Chemical and Hydrometallurgical Processes
Leaching: The remaining metal powders undergo leaching, where they are treated with chemicals to dissolve metals into a solution. This step is critical for extracting cobalt, nickel, manganese, and lithium.
Precipitation: Metals are then precipitated from the solution, forming solid compounds that can be refined further. This process recovers high-purity metals for reuse in new batteries.
Electrowinning: Some facilities employ electrowinning, an electrochemical method that deposits pure metals onto cathodes, producing high-quality materials.

Environmental Protection and Safety Measures
Pollution Control: Advanced recycling plants incorporate pollution control systems, such as air purification units and wastewater treatment facilities, to minimize environmental impact.
Safety Protocols: Stringent safety protocols are implemented throughout the recycling process to protect workers and prevent accidents. Facilities adhere to strict regulations governing hazardous materials handling.
The process of lithium ion battery recycling encompasses multiple stages, each playing a vital role in achieving efficient material recovery and environmental protection. By understanding and supporting these efforts, we contribute to a more sustainable future.